Did you know that your car’s EGR valve plays a vital role in reducing emissions and maintaining engine efficiency?
Whether you’re driving a petrol, diesel, or hybrid, understanding how this component works can help you avoid costly repairs and improve performance.
What is an EGR Valve?
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve is a crucial part of your car’s emission control system.
The EGR valve controls exhaust gas recirculation, which redirects some exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber.
This lowers combustion temperatures and reduces nitrogen oxides (NOx), keeping the air cleaner and protecting you from harmful pollutants.
What Does an EGR Valve Do?
The EGR valve reduces NOx by controlling how much exhaust gas is reintroduced into the combustion process.
For combustion to occur, your car draws in air, made up of roughly 80% nitrogen and 20% oxygen. This air mixes with fuel and ignites at high temperatures.
At these temperatures, nitrogen can react with oxygen to form nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are harmful pollutants.

By reintroducing exhaust gases, which are inert and contain less oxygen, the combustion process slows, peak temperatures drop, and NOx emissions are reduced.
The EGR valve controls this process by opening and closing. It remains closed at engine start-up and gradually opens as the engine warms. It then adjusts as needed based on engine speed and load.
Recirculation only occurs under the right conditions, helping maintain fuel efficiency while keeping emissions low.
There are two main types of EGR valve. Older vehicles use vacuum-operated systems, while modern engines rely on electronically controlled valves managed by the engine control module (ECM), using data from various sensors.
How Does EGR Work in a Diesel Engine?
Diesel engines typically operate at higher temperatures than petrol engines, making EGR systems more essential and complex.
These systems often include components like EGR coolers, which lower the exhaust gas temperature before it is recirculated into the combustion chamber.
Due to the added complexity, diesel valves are more prone to clogging and failure, especially in cars used for short trips where the engine stays cool.
How Does EGR Work in a Petrol Engine?
Diesel cars aren’t the only ones with an Exhaust Gas Recirculation valve. Most petrol and hybrid cars have them too.
In hybrid vehicles, the EGR system can improve fuel economy by up to 4.6%, especially under medium-load conditions when the internal combustion engine is running.
Electric vehicles, however, don’t need EGR valves since they produce zero tailpipe emissions.
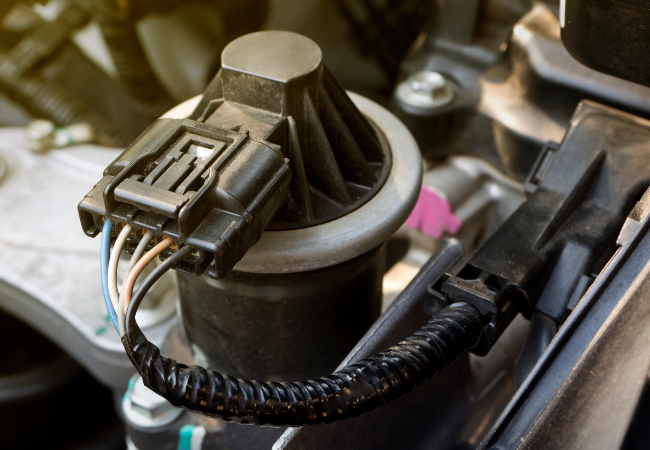

Where is the EGR Valve Located?
Most valves are positioned between the intake and exhaust manifolds.
In many vehicles, you’ll find it mounted on the driver’s side of the engine, often at the top or rear.
However, it may be hidden behind other components, making it tricky to access without removing covers or sensors.
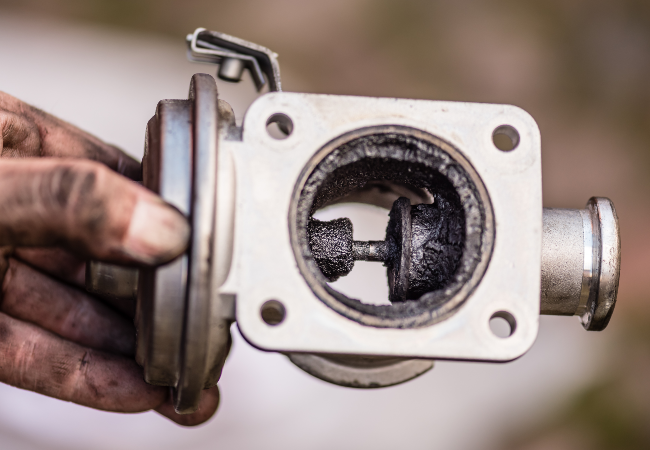
How Do You Know If Your EGR Valve Is Faulty?
A faulty EGR valve can affect engine performance, causing reduced power, slower acceleration, poor fuel economy, and higher emissions.
This often happens when the valve gets stuck open or closed due to a build-up of carbon, soot, or dirt.
Motorway driving helps prevent this by keeping the engine hot enough to burn off deposits, while short urban journeys can cause them to build up over time.
A faulty EGR valve may not always trigger an MOT failure, but it can be flagged during a service or emissions test.
Symptoms of a Faulty EGR Valve
1. Frequent Stalling
Frequent stalling is when the engine unexpectedly stops running, often while idling.
This usually happens if the EGR valve is stuck open, allowing exhaust gases to upset the air-fuel balance.
2. Rough Idling
A rough idle means the engine feels shaky or uneven when the car is stationary, such as at traffic lights or just after starting.
This often happens at low engine speeds with a warmed-up engine if the EGR valve is stuck open and lets exhaust gases into the intake at the wrong time.
3. Knocking or Pinging Noise
Knocking noises occur when premature fuel ignition happens, often because a closed EGR valve causes high combustion temperatures at low engine speeds.
Detonations, or secondary explosions after the initial ignition, can also occur in these conditions.
4. Poor Engine Performance
Poor performance means the engine struggles to deliver power smoothly, causing hesitation or sluggishness when accelerating.
This can occur if the EGR valve is stuck open or closed, disrupting the combustion process.
5. Poor Fuel Economy
Increased fuel consumption means your car uses more fuel than usual.
When the EGR valve is stuck open, cooler combustion temperatures prevent fuel from burning efficiently, causing higher fuel use.
6. Increased Emissions
Increased emissions mean your car releases more harmful gases into the environment, affecting air quality and contributing to pollution.
A stuck-open valve causes more unburned hydrocarbons, while a stuck-closed valve produces excess nitrogen oxides (NOx).
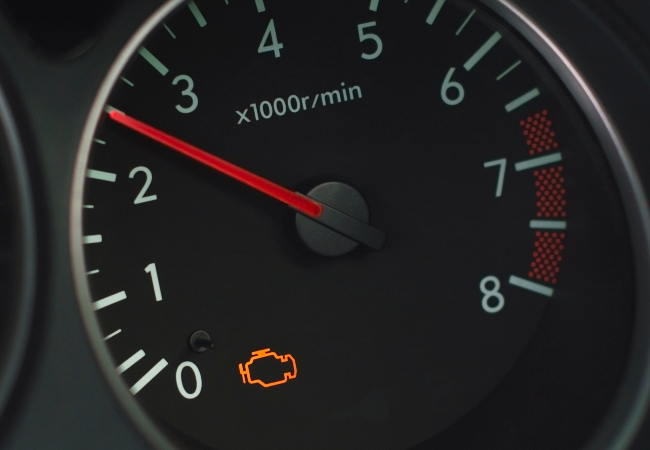

What Damage Can a Faulty EGR Valve Cause?
Ignoring a faulty EGR valve can lead to serious issues, including:
- Triggering the engine management light (EML).
- Reduced power and the car going into limp mode.
- Excessive carbon build-up in the intake manifold.
- Damage to the turbocharger, especially the VNT mechanism.
- Long-term damage to catalytic converters and diesel particulate filters (DPFs).
Early diagnosis and cleaning or replacement can prevent more expensive repairs.
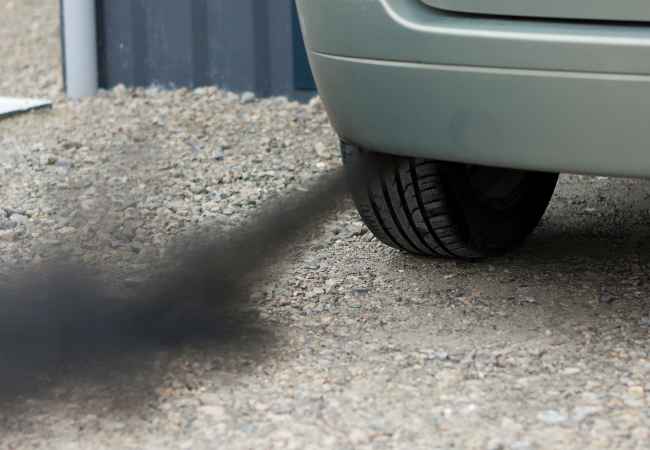
Will a Faulty EGR Valve Fail an MOT?
Yes, a faulty valve can cause your vehicle to fail its MOT test. Here’s how:
- An illuminated engine warning light is an automatic MOT failure under current regulations.
- Elevated NOx levels detected during the emissions test can also result in a failure, especially on diesel vehicles.
- Unburned fuel or increased particulates may lead to advisories or further investigation, especially if there’s visible smoke or signs of poor combustion.
Ensuring your EGR system is working properly is essential for passing your MOT and staying road legal.

But Could It Be Something Else?
Some engine problems that suggest a valve failure can also be caused by other issues, like:
- Increased emissions can occur if fuel injectors leak or inject fuel at the wrong time.
- Nitrogen oxide levels can rise due to a vacuum leak, which lets air in and disrupts the air–fuel mix.
- A rough idle can be caused by ignition system problems, such as a faulty ignition coil.
While these symptoms often point to a faulty EGR valve, they can also result from other engine issues like a failing turbocharger, diesel particulate filter (DPF), or malfunctioning sensors. That’s why it’s crucial to have a proper diagnostic done before replacing parts unnecessarily.
What to Do If You Suspect a Faulty EGR Valve
1. Clean the EGR Valve
Carbon build-up is a common cause of EGR issues. Remove the valve and carefully clean it using an EGR cleaner, taking care not to damage the diaphragm. Also, check the passage and EGR cooler for blockages and clean if needed.
2. Get a Proper Diagnosis
If symptoms persist, like stalling, rough idling, or increased emissions, book a diagnostic check with a qualified mechanic. EGR faults can be confirmed using the right equipment, helping you to avoid any unnecessary repairs.
3. Replace the Valve if Necessary
If cleaning doesn’t fix the problem, you may need to replace the Exhaust Gas Recirculation valve. Some manufacturers also recommend EGR valve replacement at set intervals, so check your owner’s manual and follow service guidelines to keep your car running at its best!
Need Help with Your EGR Valve?
If a dashboard warning light is on or you’re noticing signs of a faulty EGR valve, don’t wait. Call our Service Team on 01405 801801 to book a diagnostic check.
We can diagnose, clean, or replace the valve to get your vehicle running smoothly again.